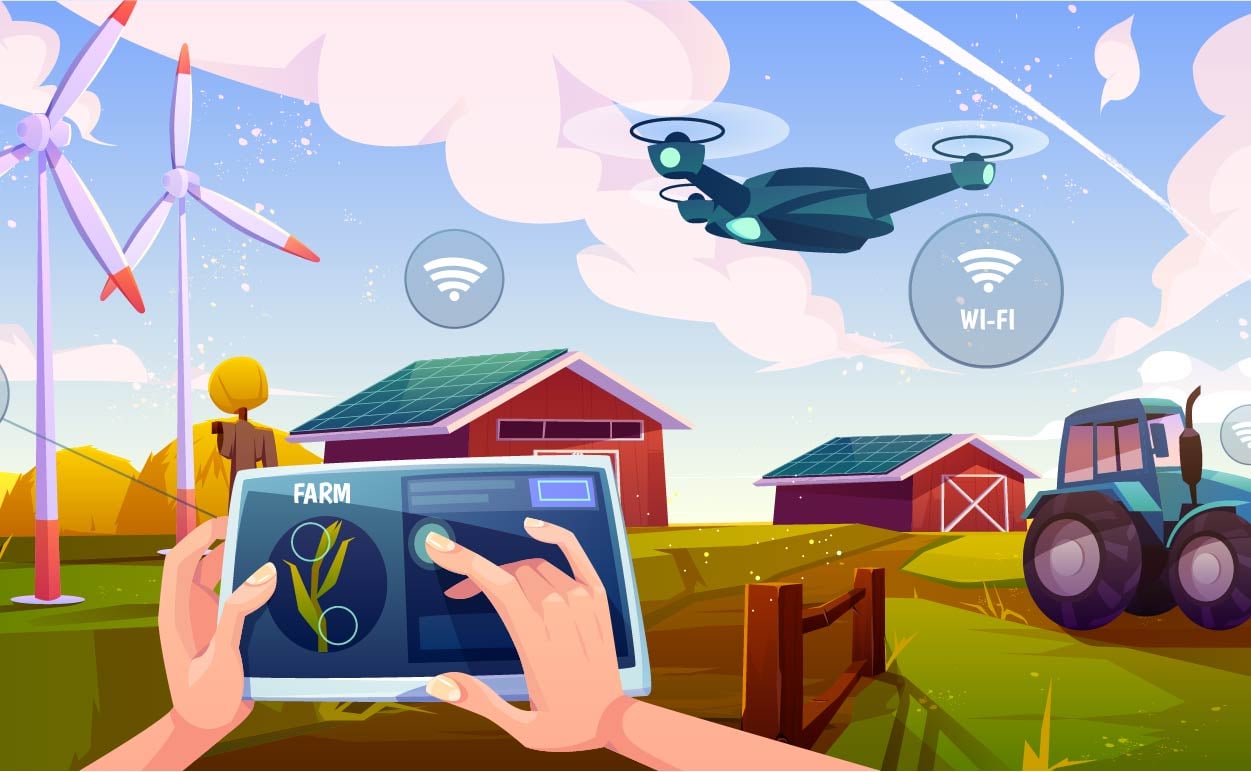
Agriculture is one of the domains set to reap significant benefits from IoT.
Internet of Things as a cornerstone of Agriculture 4.0
The challenges associated with food production become a growingly relevant theme. It is projected by the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) that by 2050, the global population will reach 10 billion people. The organization warned that to keep pace with such a rise in global population, food production would need to increase by 70%. Additionally, the accelerating urbanization process reduces labor in regions typically devoted to food production.
To surmount such challenges, agricultural firms and farmers are turning to Agriculture 4.0. IoT appears to be a promising technology capable of contributing to the optimization of agricultural processes. Indeed, agriculture IoT market is projected to be worth $34.9 billion by 2027, according to Meticulous Research.
Here are three ways IoT solutions can help the agriculture sector overcome these obstacles:
Changing the paradigm of greenhouses
In comparison with open-field agriculture, protected agriculture, entails a more controllable internal environment for crop growth by adopting greenhouse technology. To a certain extent, protected agriculture is not subject to the constraints of the environment and enables the effective exploitation of agricultural resources. Nonetheless, in protected crops, temporal and spatial variability of environmental parameters are strong and influence each other. This poses a great challenge for farmers as different types of plants have different growth stages and different environmental requirements. Accordingly, protected agriculture requires higher accuracy and extra effort in terms of monitoring and control.
That’s where IoT enters the scene. One of the technical bottlenecks in the development of the IoT system is the sensor systems. Smart greenhouses would utilize IoT-powered sensors to monitor the internal environment that is favorable for thecrop. Particularly, sensors are installed to measure conditions such as temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, leaf wetness, light levels. Enabled by IoT, the sensors can be connected to the cloud via satellite or cellular network. Therefore, farmers could gain access to real-time data concerning the climate conditions of their greenhouses and take timely preventive measures to protect the plants. Additionally, an IoT-powered greenhouse could predict, for instance, the crop water needs and make recommendations on when to irrigate and how many nutrients to apply.
Optimizing livestock management
Day-to-day monitoring of livestock condition is relatively arduous, especially in large farms. IoT seems to be one of the remedies for the issue by enabling farmers to closely monitor the health of their livestock in real-time while reducing labor costs. Specifically, connected sensors in livestock wearables could constantly measure each animal’s conditions like heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, etc. When a cow’s temperature reaches an abnormal level, the system would automatically trigger an alert via messages allows a timely response, which eventually helps farmers to reduce medical costs.
In addition, the IoT technology could feature potential benefits in fertility monitoring. For example, there have been use cases of an IoT-based cow reproductive health monitoring system. The automated system could detect changes in cow behaviors that suggest estrus. The sensors might also be conducive to tracking the herd's present whereabouts for optimized grazing patterns.
Elevating the agri-food supply chain
As governments in several countries have been promulgating laws to boost the supervision of agricultural products, there has been an increasing need for agri-food supply chain traceability.The food supply chain is attributable to the involvement of perishable products. Accordingly, there is a strict need to maintain specified environmental conditions from farms to stores/table. The IoT technology functions as a useful tool in the food supply chain due to its end-to-end visibility. Sensors are used to constantly keep track of temperature, humidity and any other conditions that cause harm to the perishability of the products. If any factor changes beyond the set threshold, shippers will receive a warning.
Smart agriculture gadgets powered by IoT can provide added values to the agricultural domain by helping farmers to overcome the challenges posed by the increasing need for food security and the lack of labor force.
Interested in more technology articles? Click here to learn more!
References
Business Insider (2020). Smart Farming in 2020: How IoT sensors are creating a more efficient precision agriculture industry.
Fastellini and Schillaci (2020). Precision farming and IoT case studies across the world.
Shi et al. (2019). State-of-the-Art Internet of Things in Protected Agriculture.