Despite being initially introduced in 1950 and undergoing around 70 years of development, Virtual Healthcare only recently gained momentum after the pandemic. Amid the COVID-19 crisis, a significant increase in demand for virtual health services has been recorded as in-person hospital visits globally dropped 50 percent during 2019-2020 [1]. While patients' skepticism and communication malfunction are the main challenges in virtual healthcare, this technology trend still thrives for its significant benefits to the care providers, prompting a remarkable 94% in customer return rate [2].
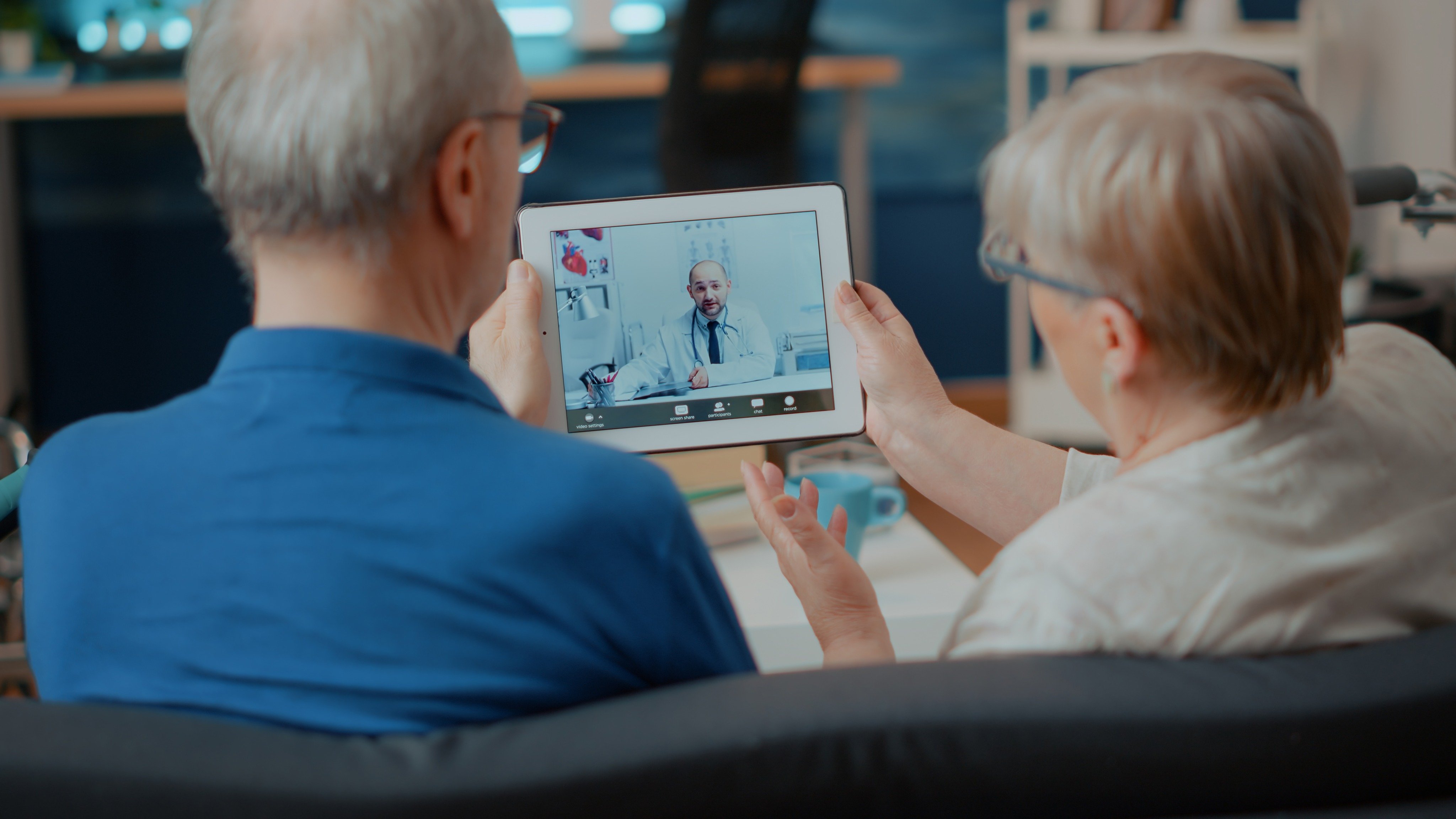
A Closeup of Virtual Healthcare
At the heart of virtual healthcare lies a fundamental objective: to enhance communication between healthcare providers and patients. By leveraging technology, virtual healthcare enables seamless, simultaneous, and consistent interactions, empowering individuals to access quality care from anywhere at any time. Moreover, Virtual Healthcare caters to diverse user groups, addressing specific needs and ensuring equitable access to healthcare services. Key user groups that benefit from virtual healthcare include rural and minority communities, the aging population, and closeted LGBTQ+ individuals,...
According to Deloitte, embracing virtual healthcare opens new avenues for business growth by 25% each year, and its global market share is expected to reach a booming US$100 billion by 2025 [3]. This expectation is based on the majority of industry-wide benefits available for patients, caretakers, and businesses. Virtual healthcare also plays a critical role in emergencies and disease outbreaks by enabling healthcare services to be provided remotely. This technology application minimizes the risk of spreading contagious diseases and avoids unexpected contamination control expenses.
For patients, healthcare businesses can reach a wider audience by providing services beyond physical boundaries. As mentioned, patients with geographic distance or privacy concerns may perceive virtual healthcare as more confidentially optimized and easily accessible. Such easier access to virtual healthcare can abridge the physical distance, global economic, and resources gap, inducing health equity. For instance, young patients are generally concerned about confidentiality in addressing their health condition, especially those related to STIs diagnoses or genital exposure [4]. Understanding these privacy concerns, virtual healthcare entities can provide cryptographic diagnoses and pre-treatment without divulging personal information or the patient's face.
In the bargain, companies that offer virtual healthcare options can show their priority on the well-being and productivity of employees. Convenient access to healthcare resources reduces employees' time and effort in commuting. This simple time efficiency perk fosters employee morale, loyalty, and retention. Amidst the crash-and-burn global shortage of the healthcare labor force, employee satisfaction and retention are indisputably important. The COVID-19 pandemic has indeed annotated this already severe lack of global medical staffing that only virtual care can unfold. The International Council of Nurses (ICN) has estimated that the world could face a shortage of 13 million nurses by 2030 unless action is taken to address attrition and attract recruits into the healthcare workforce [5].
To businesses worldwide, the prominent advantage of virtual healthcare is scalability, flexibility, enhanced cost, and time management: virtual care eliminates the need for inpatient housing expenses, reducing the time and costs associated with routine check-ups. Moreover, healthcare providers extend their services beyond geographical limitations. Care services can aptly reach patients in remote or underserved areas, providing access to healthcare services that may otherwise be unavailable. This opens up new market opportunities and expands the provider's reach. Additionally, virtual care offers flexibility for doctors and employees, allowing them to achieve a better work-life balance. They can schedule consultations and appointments according to availability, reducing stress and improving job satisfaction.
Navigating the Global Challenges of Virtual Healthcare
The rapid advancement of virtual healthcare has transformed how healthcare services are delivered worldwide. While it presents numerous benefits, there are several challenges that business owners in the virtual healthcare space must address.
- Cybersecurity risk
According to the Cyber Peace Institute, 400 cyberattacks were recorded in over 40 countries worldwide within the last two years (2021-2023). These attacks can disrupt healthcare operations and steal over 10 million records, raising ransomware concerns about virtual healthcare [6]. The dark web's interest in this stolen medical information poses a significant risk to patients' financial safety and businesses' privacy lawsuits. Medical records contain valuable information such as Social Security numbers, medical history, treatment information (business know-how), and payment details [7]. Unauthorized access or disclosure of health information can be just as dangerous as ransomware attacks, and negligence by providers and employees can lead to patient data exposure.
- Bridging Geographical Gaps
Bridging geographical gaps in virtual healthcare is an essential and trendy topic that has gained significant attention, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. These challenges can be categorized into physical distance and cultural distance. Regarding physical distance, virtual healthcare aims to provide healthcare services to individuals in different locations. However, this poses challenges related to infrastructure, connectivity, and access to technology. In some remote areas, less internet connectivity or inadequate technology infrastructure may hinder the effective delivery of virtual healthcare services. In addition, psychological, cultural, and language barriers can significantly impact the understanding between healthcare providers and patients. These barriers can hinder effective information exchange, impede accurate diagnosis and treatment, and potentially result in suboptimal healthcare outcomes.
Virtual healthcare has the potential to bridge geographical gaps and provide easy access to healthcare resources globally. However, challenges persist in having efficient technology to overcome physical and psychological barriers.
Super Apps - The Ultimate Solution for Virtual Healthcare Conundrum
As virtual health services face the hurdle of payer-provider distance and regulations, implementing a super app is crucial in tackling these challenges. Amwell, Teladoc Health, or Babylon Health are prominent virtual healthcare super apps remotely offering all patient-centric services in one digital platform. They go beyond the scope of traditional telemedicine by providing a more extensive range of features and benefits, encompassing primary care, specialty care, and wellness programs. Upon patient demand, a super app can arrange efficient doctors for specific patients' needs and demographic backgrounds, avoiding regulatory and cultural conflicts. In addition, super apps can help safeguard sensitive patient data from unauthorized access by implementing encryption protocols, user authentication mechanisms, and anonymization techniques. Demonstrating such commitment to data protection, healthcare providers can eventually build trust among users who value the confidentiality of their health and personal information.
With AI/ML, Automation, Data analytics, and other next-gen technologies, digital communication is made more accessible than ever. AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants help users from both ends to respond instantly to common healthcare inquiries, receive personalized recommendations, and access basic healthcare information. Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms enable these virtual assistants to understand user queries and provide relevant responses. In addition, implementations such as AI translators bridge the gap by providing real-time language translation that not only enhances accessibility but also ensures that language differences do not impede quality healthcare delivery. Besides, data analytics can analyze user preferences, behaviors, and medical history to generate personalized recommendations for health-related services, such as medication reminders, health tips, and preventive screenings. The healthcare super app can enhance user engagement and facilitate better understanding, diagnosis, and treatment by tailoring recommendations based on individual needs.
Conclusion
Virtual healthcare has emerged as a transformative approach. However, virtual care must go beyond basic telemedicine practices and embrace the integration of high-technology medical instruments and applications to engage patients empathetically. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge technologies, virtual care has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, ensuring accessibility, convenience, and personalized experiences for patients worldwide. The full potential of virtual care can be realized through this combination of human touch and technological innovation, transforming the future of healthcare.