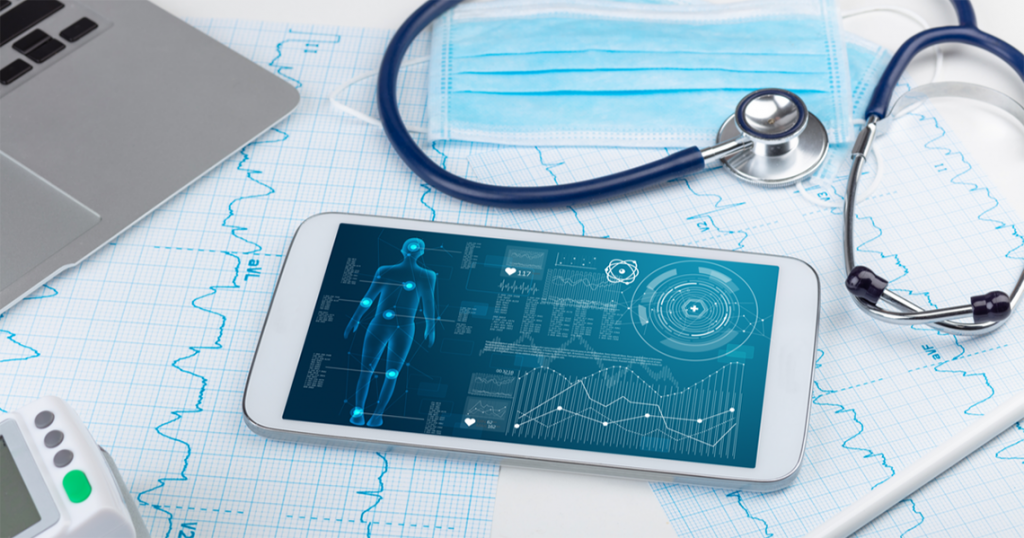
In today's era of groundbreaking innovations, where the lines between healthcare and technology increasingly blur, one term has generated substantial buzz: Software as a Medical Device, or SaMD. Delving into the intricate world of SaMD, this article sheds light on its growing significance, capabilities, and potential.
Defining SaMD
As the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) endorsed, SaMD is a standalone software with a clear medical intent. In simpler terms, it’s software designed for medical applications without the need to be part of a physical medical device.
For context, a healthcare provider's smartphone app displaying MRI images is SaMD. In contrast, the embedded software within the MRI machine is not.
Characteristics of SaMD:
- Independence from Hardware: SaMD works without being tethered to a specific medical device. It can interact with various tools, data, the internet, or other SaMDs.
- Medical Functionality: Although software may interact with medical data, this doesn't automatically label it as SaMD. Its primary function must be medical in nature.
- Variety of Platforms: From desktop applications to algorithms on cloud infrastructure, SaMD can exist anywhere.
Types of Medical Device Software:
- Software in a Medical Device (SiMD): Embedded software in medical equipment.
- Accessory Software: Complements a medical device but doesn't function as one.
- General-purpose Software: Not primarily designed for medical purposes.
Why is SaMD Relevant Today?
The surge in SaMD's popularity is tied to the explosion of IoT devices, enhanced connectivity, powerful mobile devices, and expansive cloud capabilities. The more data these devices produce, the more precise and effective SaMD becomes.
Moreover, the market for SaMD is expanding rapidly. Expected to reach a whopping $86 Billion by 2027, up from $18 Billion in 2019, it's ushering in a new age of medical solutions.
SaMD in Action:
- Screening & Diagnosis: Algorithms can predict chronic diseases and enable quicker treatments.
- Chronic Condition Management: SaMDs can track health metrics for improved personalized treatments.
- Monitoring & Alerting: Wearable sensors, when combined with SaMD, can actively monitor vital signs.
- Digital Therapeutics: Address chronic illnesses like sleep apnea using SaMD combined with smart device features.
The Promise of SaMD for the Future
SaMD has the potential to revolutionize healthcare:
- Data-Driven Health Outcomes: Enhanced data collection can boost the effectiveness of medical treatments.
- Speedy Innovations: SaMD can be updated and improved rapidly, leading to swift advancements in medical technology.
- Aiding the Physician Shortage: The increasing demand for physicians can be mitigated, to some extent, with SaMD tools, ensuring a more efficient healthcare system.
The world is only beginning to scratch the surface of what SaMD can achieve. As technological advancements continue to converge with healthcare needs, SaMD will undoubtedly play an instrumental role in shaping the future of global health. It represents not just the synergy of software and medicine but the promise of a healthier tomorrow. To learn more, view our whitepaper What is Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)?