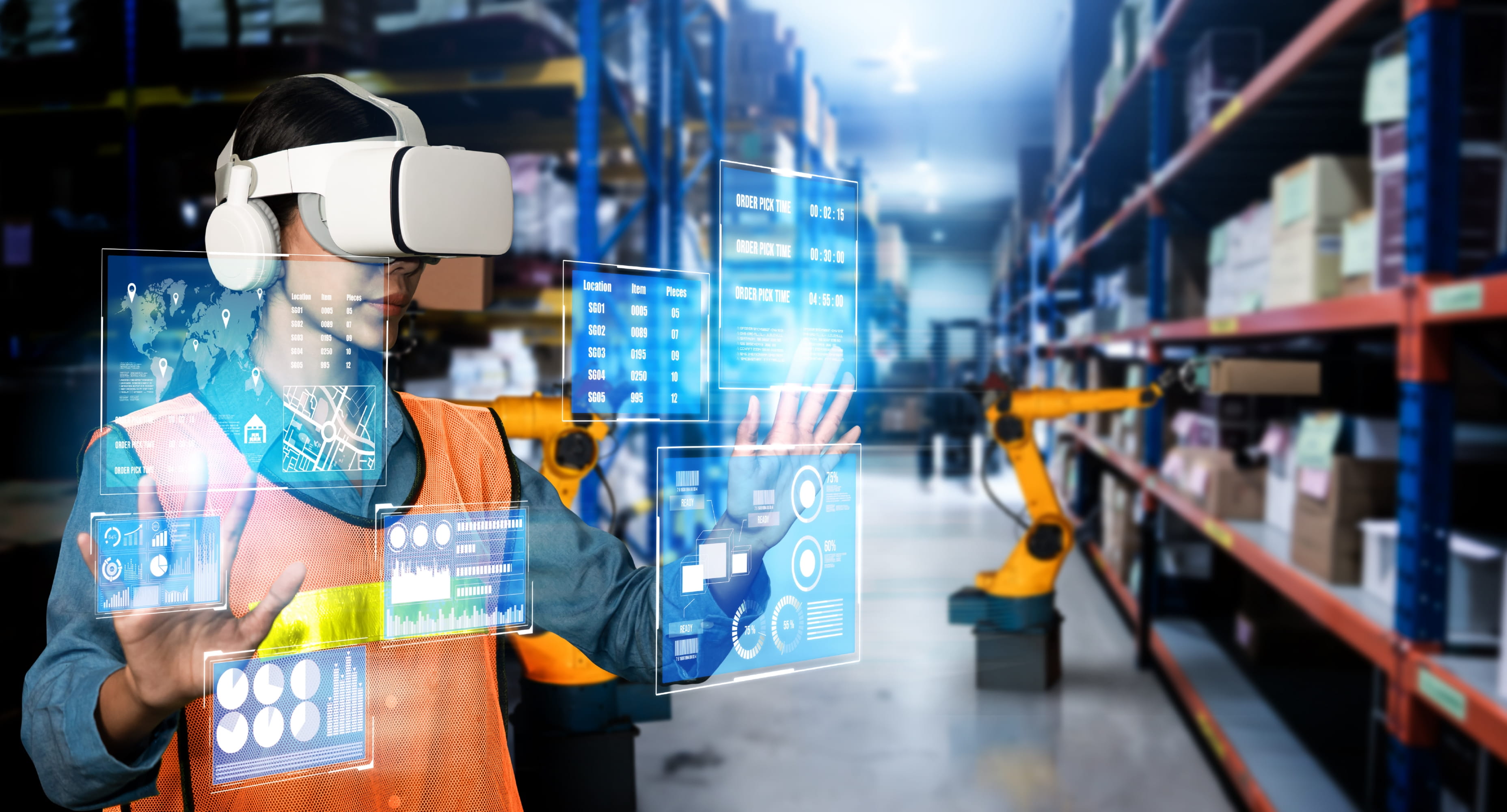
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have emerged as powerful tools with immense potential, particularly in industrial manufacturing and design. Research by PwC highlights the tremendous opportunities offered by leveraging VR and AR in product and service development, projecting a remarkable USD 360 billion GDP boost by 2030 [1]. For the manufacturing industry, these technologies bring a multitude of advantages, including:
- Improving collaboration;
- Enhancing product prototyping;
- Facilitating efficient maintenance practices; and
- Providing accessible training.
Facilitate teamwork and collaboration
AR/VR technologies can enhance collaboration in the manufacturing industry through the creation of virtual shared spaces where geographically dispersed teams can converge. Team members can share insights and provide feedback through real-time communication features such as voice chat, video conferencing, and instant messaging. The 3D visualization capabilities of AR/VR further enhance collaboration by enabling users to manipulate complex 3D models with natural movements and gestures. According to research, 72% of respondents indicated improved collaboration ranks among the top four advantages of using AR in the workplace [8].
Furthermore, AR/VR systems offer multi-user functionality, as their cross-platform compatibility ensures accessibility for all team members. Team members can seamlessly join collaborative sessions by using VR headsets, AR glasses, or desktop computers. For instance, when faced with complex technical issues, on-site personnel can use AR/VR devices to connect with off-site experts in real time. The remote expert can virtually see what the on-site personnel sees through their device's camera and provide helpful information, 3D models, or instructions applied to the real-world environment.
The use of AR/VR has been widely adopted by manufacturing corporations. One notable example is Honda, which utilized the advances of VR and AR to enhance the quality and appeal of its products: the all-electric 2024 Honda Prologue and the 2023 Honda Pilot TrailSport. VR ensured smooth progress in the Prologue design development and bolstered the team's capabilities for future projects. Although traditional design processes were still in use in the designing process, VR and AR technology took center stage in executing the interior design. This, in turn, assisted the team in developing designs more cohesively.
Bringing products to life
In the past, 2D visualization and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) were the cornerstones of the manufacturing industry. However, these tools may fall short of fully capturing the reality of the product. The absence of thorough validation in a virtual environment increases the risk of encountering design flaws and costly rework. Of the estimated USD 140 billion spent on new product development by large companies each year, failed products comprise 40% of the cost [2].
AR and VR can streamline the designing process by visualizing prototypes, simplifying complex assemblies, and exploring options to validate feasibility. Compared to traditional physical prototyping, AR and VR can save both time and money. Companies in the manufacturing sector are aware that a single physical prototype can cost up to $30,000 [3]. With the help of AR/VR technology tools, companies can create, test, and adjust before the production of the physical prototype through virtual means. Realistic simulations and testing in various scenarios help engineers detect design flaws and performance issues easily.
To be specific, engineers can visualize product designs in a 3D virtual environment, providing a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and proportions. AR/VR enables designers to create detailed 3D models of products using CAD software through advanced computer graphics and real-time rendering technologies. While AR uses camera sensors and tracking systems to provide users information for real-world application, VR immerses users in entirely virtual environments through specialized headsets and controllers. Designers and engineers can interact with these virtual prototypes using hand gestures, controllers, or eye-tracking devices, allowing them to move, rotate, and manipulate the product.
Maintenance is no longer a challenge
Detecting potential issues and conducting timely repairs can be complex tasks. Particularly, 93% of companies acknowledge that their maintenance processes are far from efficient [5]. Unforeseen downtime caused by equipment failures resulted in substantial financial losses and disrupted supply chains. Indeed, it is estimated that unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers a staggering USD 50 billion annually [6]. Thus, by using AR-powered maintenance applications, technicians can access with real-time data, diagnostics, and maintenance instructions. Furthermore, AR/VR can provide visual guides for repairs and offer access to technical manuals without the need for physical copies. This visual guidance simplifies the repair process, making it more accessible even for less experienced technicians.
Training made accessible
The use of VR headsets helps bridge the skill gap for maintenance technicians. This is important for companies dealing with talent shortages caused by experienced workers retiring with years of expertise. Specifically, McKinsey's research shows that 43% of organizations currently face skill gaps, and another 44% expect a skills shortage in the next five years [6]. Besides, VR training is easily accessible anytime and anywhere, allowing technicians to practice on their schedule until they master the necessary skills.
Within the virtual environment, technicians can reduce errors and potential accidents by familiarizing themselves with the equipment before arriving at the job site. In addition, VR immerses trainees in life-size simulations of industrial plants without exposing themselves to risks. A PwC survey revealed that 51% of businesses had a VR training strategy or were actively working to implement one [7]. The virtual training platform can be reused over the years, thus reduce training costs in the long run.
Grasping the opportunities
Despite the clear potential for significant improvements in design and production processes through VR/AR solutions, their adoption in manufacturing remains limited. Many business leaders are unaware of the numerous use cases and benefits that AR/VR implementation can bring to their operations. While technology can revolutionize the manufacturing industry, studies indicated that 25% of manufacturers remain uncertain about the implementation process [9]. Nevertheless, there is ample time and opportunity for manufacturers to capitalize on the advantages offered by VR/AR technology in their operations.